Google Expands Android Sharing
Google is increasing its cross-device sharing features to include more Android users, delivering better connectivity and ease. Initially unveiled at Google I/O 2024, these capabilities include call casting and internet sharing, revolutionizing how Android devices interact. Find out everything about the deployment, its ramifications, and how to use these features successfully.
Introduction
Google has long been at the forefront of technological innovation, continually improving its Android ecosystem to boost user experience. In May 2024, at the Google I/O developer conference, the tech giant revealed a suite of cross-device sharing features designed at making Android devices more integrated and user-friendly. These features, which allow seamless sharing of conversations and internet connections across many Android devices, signal another key milestone in Google’s ambition of a fully linked tech ecosystem. As of today, Google is providing these features to more consumers, particularly those with smartphones running Android 11 and above.

Initially limited to select devices like Pixel and Samsung Galaxy models, the spread of these functionalities is now gaining steam with the current update (version 24.35.30) of Google Play Services. This essay goes deep into Google’s cross-device sharing features, analyzing their functionality, availability, and the possible influence on the Android environment.
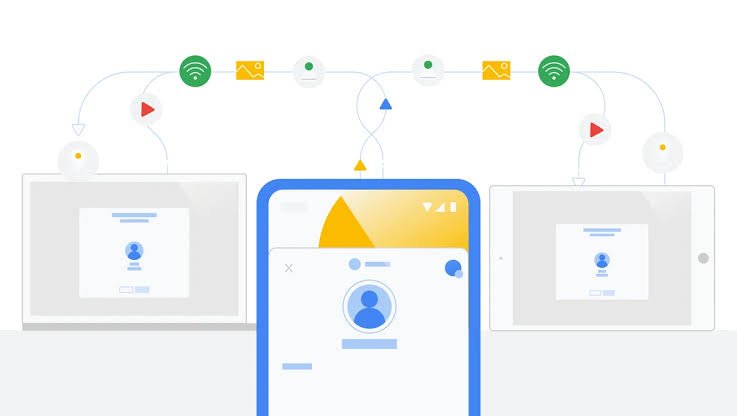
What Are Cross-Device Sharing Features?
Cross-device sharing refers to the capacity to share content and functionalities—such as calls, data, and other services—across several devices effortlessly. For Android users, this means that numerous devices tied to the same Google account may converse and share data simply, removing the need for redundant setups and configurations.
Key Features of Google’s Cross-Device Services
- Call Casting
Call casting allows users to transfer audio or video calls from one Android smartphone to another. This feature is especially handy for people who use multiple devices, such as a phone and a tablet or smartwatch. It presently supports Google Meet, letting users to switch devices mid-call without interruption. - Internet Sharing
Google has also provided internet sharing between Android devices without the requirement for typical Wi-Fi passwords. As long as the devices are signed in to the same Google Account, users can share their internet connection with linked Android devices or Chromebooks.
These developments show Google’s dedication to making Android a more coherent platform. Both features are designed to boost productivity and convenience, particularly for those who rely on numerous devices daily.
The Rollout of Cross-Device Features
The implementation of these cross-device sharing features is already underway, with Google working on assuring compatibility across various Android devices. The features are available for devices running Android 11 and above, including a wide range of Pixel and Samsung Galaxy models. The update is being rolled out gradually with version 24.35.30 of Google Play Services.
Devices Compatible with Cross-Device Sharing
The following devices are the key targets of Google’s latest cross-device features:
- Pixel Devices
Google’s own line of Pixel smartphones is often the first to receive Android updates, and the cross-device features are no exception. Pixel users running Android 11 or later can access these capabilities through the Google Play Services upgrade. - Samsung Galaxy Devices
Samsung, a longstanding collaborator of Google, has also been prioritized in the deployment. Galaxy smartphones running Android 11 or above are set to benefit from these cross-device functionalities. - Other Android Devices
Although the initial focus has been on Pixel and Galaxy smartphones, Google wants to increase the availability of these features to other Android devices in future updates.
Setting Up Cross-Device Sharing: A Step-by-Step Guide
Accessing and exploiting cross-device sharing features is quite simple. Here’s how consumers may enable and use these features on their Android devices:
- Go to the Settings App Open the Settings app on your Android device.
- Select Google
Scroll down and select the “Google” option under the settings menu. - Navigate to Devices & Sharing
Under the Google settings, tap on “Devices & Sharing.” - Choose Cross-Device Services
In the Devices & Sharing menu, pick “Cross-Device Services” to explore the available sharing options. - Set Up Your Device Group
To enable cross-device functionalities, users must create a device group. This entails activating preferences on all devices enrolled into the same Google Account. - Manage Feature Preferences
Users can toggle particular functions on or off, such as call casting or internet sharing. Devices that are part of the group will be listed under “Your other devices,” reflecting what has been “Added” or “Not added.”
How Call Casting Works
One of the most fascinating elements of Google’s cross-device services is Call Casting. This feature allows users to easily transfer ongoing voice or video calls between Android devices logged into the same Google Account. Imagine making a video call on your phone and then moving to a tablet or Chromebook without any disturbance to the conversation. Here’s how it works:

- Initiate a Call
The capability is initially confined to Google Meet, so you’ll need to start a video call on one of your Android devices using the app. - Cast the Call
During the call, touch on the “Cast” icon, which will appear on the Google Meet interface. This will show up a list of devices connected to the same Google account. - Choose Your Device
Select the device to which you want to transfer the call. The call will then automatically switch to the new device, allowing you to continue the chat without interruption.
Benefits of Call Casting
- Seamless Transitions
Call casting enables users to transfer between devices effortlessly, which can be very handy in multitasking settings. For example, you may begin a conference on your phone while commuting and then complete it on a larger screen when you reach at your destination. - Device Flexibility
The functionality allows customers the flexibility to switch between devices depending on their needs. For instance, video calls can be more comfortable on a tablet or laptop, while audio calls might be best managed on a phone.
How Internet Sharing Works
The second significant element of Google’s cross-device services is Internet Sharing, which allows users to share their phone’s internet connection with other devices in the same Google Account group, such as Chromebooks and other Android smartphones.
Steps to Use Internet Sharing
- Enable Bluetooth and Location Services
To share your phone’s internet connection with another device, make sure that both Bluetooth and location services are turned on. - Go to Settings > Google > Devices & Sharing
Similar to call casting, the ability to share your internet connection may be found under “Devices & Sharing” in the Google settings. - Activate Internet Sharing
Toggle on the “Internet Sharing” function. Your phone will now be able to share its internet connection with other devices in your Google Account group. - Connect the Other Device
The receiving device will instantly recognize the internet-sharing option, and users can connect without the need for Wi-Fi passwords or hotspot configurations.
Benefits of Internet Sharing
- No Need for Passwords
Traditional hotspot settings need users to enter passwords and go through a series of processes. With cross-device internet sharing, the procedure is simplified, making it faster and easier to share connectivity across devices. - Works Across Devices with the Same Google Account
As long as the devices are logged into the same Google Account, they can smoothly share internet connections. This feature is particularly handy for users that move between devices regularly, such as students or professionals working on numerous platforms.
Why Google’s Cross-Device Features Matter
Google’s extension of cross-device sharing options is more than simply a convenience—it’s a purposeful move to consolidate Android’s status as a versatile, connected platform. In a world where individuals use numerous devices everyday, regularly jumping between phones, tablets, laptops, and smartwatches, seamless device interaction is becoming increasingly critical.
Enhancing User Productivity
The ability to cast calls and share internet connections without any disruptions or complex installations allows users to remain working across numerous devices. Whether for personal or commercial use, the capabilities save time and decrease the friction associated with managing several gadgets.
Competitive Edge Over Apple
Google’s cross-device sharing services match Apple’s Handoff function, which allows Apple customers to shift tasks across iPhones, iPads, and MacBooks. By bringing similar functionalities to Android, Google is leveling the playing field and potentially luring customers who appreciate such integrated experiences.
Integration with Google Ecosystem
These features better integrate Android smartphones into the greater Google ecosystem. With Android commanding a significant share of the worldwide smartphone industry, cross-device sharing services may attract additional customers to invest in Android-powered devices, further strengthening Google’s dominance.
The Future of Cross-Device Sharing
While call casting and internet sharing are the key aspects of Google’s current cross-device services, the company has hinted at future developments. As the features expand, we may expect more functionality like file sharing, app continuity (the ability to continue using an app on another device), and even more sophisticated connection with Google Workspace and other productivity tools.
The Role of AI in Cross-Device Features
Given Google’s concentration on AI, it’s probable that future incarnations of cross-device sharing will use machine learning to anticipate user demands. For example, AI may automatically propose moving a call to a different device based on user behavior patterns, or intelligently manage internet usage across devices.
Conclusion

Google’s extension of cross-device sharing tools marks a new era of connectivity for Android users. By permitting seamless transitions between calls and easy internet sharing across devices, Google is fulfilling a fundamental need in today’s multi-device environment. With regular updates and the potential for further features, the future of Android looks increasingly integrated, making life easier for users who rely on many devices throughout the day.
As the deployment develops, more Android users will be able to enjoy the convenience and efficiency of these cross-device services, increasing both personal and professional productivity. For now, consumers can look forward to an Android environment that is more unified, functional, and integrated than ever before.